UX LENS
News and Tips
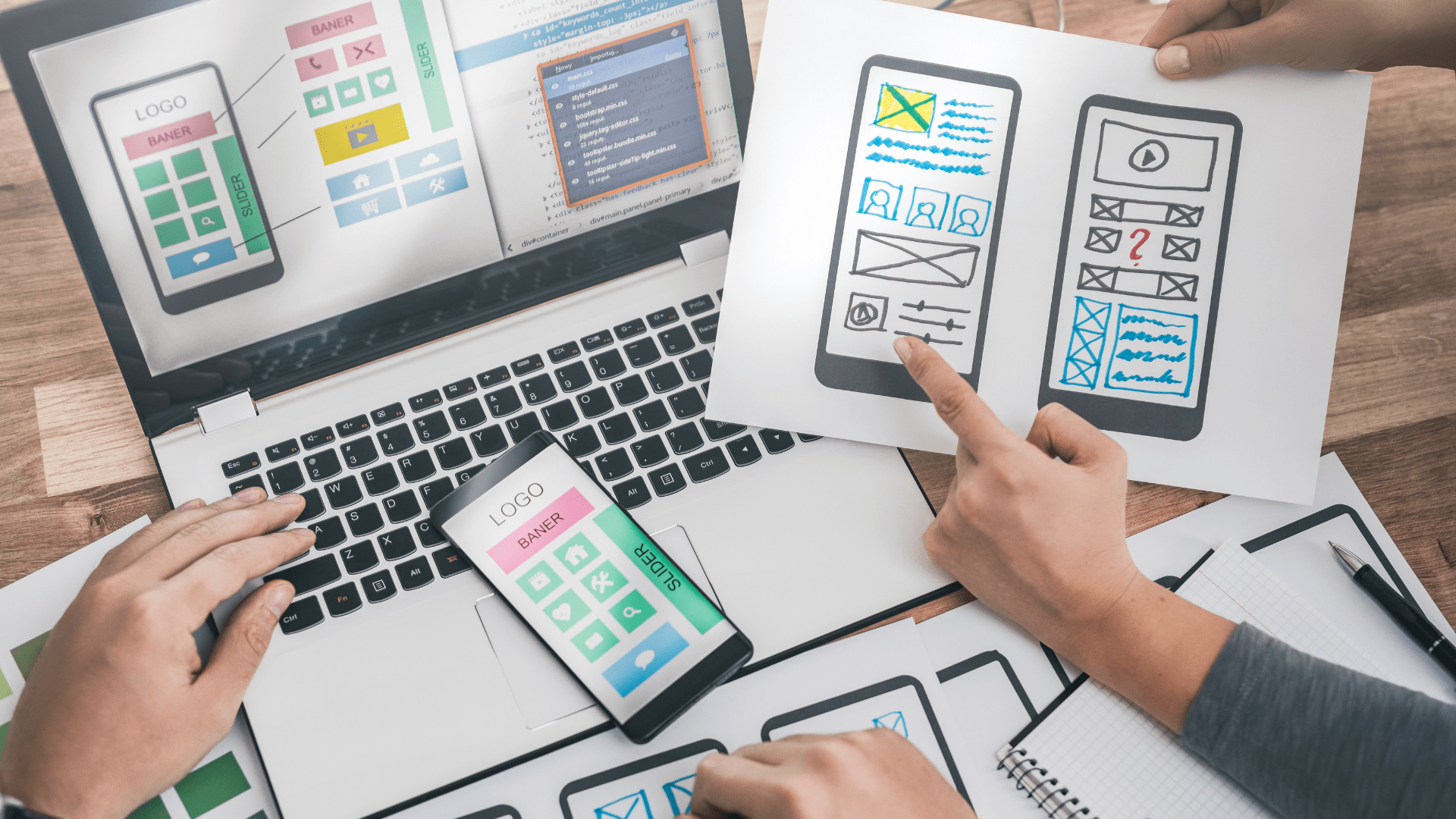

Enterprise Software UX Design
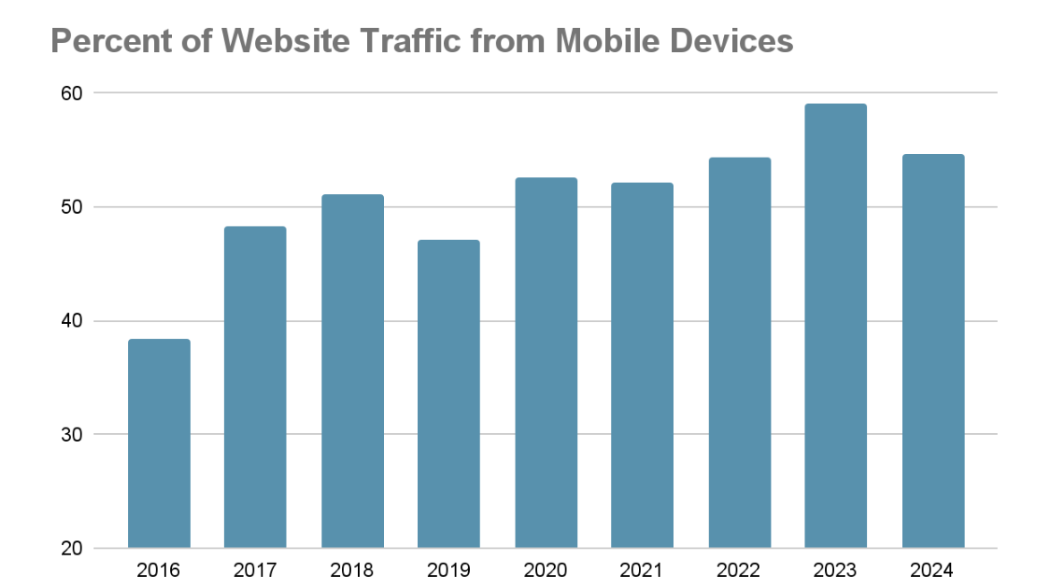
The Statista report states that. 54.67% traffic comes from mobile devices in Q4 of 2024. User friendly design majorly influenced this, faster loading times and mobile friendly layouts.
Let us see one more stats..
The Design Management Institutes tudies shows the UX design companies helped in outperforming SP 500 companies by 228% over the last years.
This further establishes UX design understands users better and makes them feel we care for you. Thus, brand loyalty translates into dollar signs.
This can be further explained through this blog.But before that, you need to understand Enterprise Software UX Design.
What is Enterprise Software UX design?
The Enterprise software UX design enhances user experience in system and software applications with eye on business needs.
Why does Enterprise UX matter?
Enterprise Software UX Design solves this problem differently by explaining it from the customer service person’s point of view. In the service centre, a customer raises a complaint. The customer service person then retrieves the customer details from the CRM and the plans details from another platform. This process can be tiring as they go back and forth.
How does Enterprise UX solve this problem differently?
The enterprise UX helps in streamline the process in a single tool thus resulting in
- Short business process with less room for errors.
- Efficient in customer and customer service person, thus resulting in providing better services.
- Less training for employees
As you got a gist about it. Let us further understand with more statistics
- According to WebFX, 94% of a brand website’s first impressions are related to design.
- According to Business Research Insights, the size of the worldwide UI market reached almost $1.6 billion in 2021 to $3.693 billion by 2028, exhibiting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 15.01%. Similarly, the global UX market, valued at $6,120.44 million in 2021, is forecasted to expand to $20,058 million by 2028, with a projected CAGR of 16.24%.
- Almost half (48%) say the number one way they decide on the credibility of a business is determined by the web design
- The Zippa report states that “38% of users won’t engage with a website if its layout is unattractive”
- According to a survey of top design firms, 50% of them consider website design for brand selection.
What are the strategies used in Enterprise software design?
UX design is used for complex enterprise software solutions that require a deep understanding of the intricate workflows, diverse user roles, and unique challenges inherent in such environments. Here are some specific strategies tailored to address these complexities:
- User Research and Persona Development:
Conduct rigorous user research to understand the needs, goals, and pain points of distinct user roles within the organisation. Create detailed user personas representing various stakeholders, including end-users, administrators, and decision-makers.
- Task Analysis and Workflow Mapping:
Analyse the complex workflows and business processes involved in the enterprise. Map out user journeys and identify key touchpoints where the software can streamline tasks, reduce friction, and improve productivity.
- Hierarchical Information Architecture:
Design a clear and intuitive information architecture that reflects the hierarchical structure of the enterprise. Organise features, modules, and data in a logical manner, for users to navigate easily and locate information relevant to their tasks.
- Customizable Dashboards and Views:
Provide users with customizable dashboards and views that allow them to personalise their workspace according to their preferences and priorities. Enable users to configure widgets, charts, and data tables to display the information most relevant to their roles.
- Contextual Awareness and Adaptive Interfaces:
Build interfaces that adapt dynamically based on the user’s context, preferences, and permissions. Surface relevant information and features based on the user’s current task, location within the software, and role within the organisation.
- Assistive Technologies and Accessibility:
Ensure that the software is accessible to users with disabilities by following standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). Provide support for assistive technologies such as screen readers, keyboard navigation, and voice commands.
- Progressive Disclosure and Guided Onboarding:
Employ progressive disclosure techniques to reveal complexity as users become more familiar with the software. Offer guided onboarding experiences and contextual tooltips to help users learn how to use advanced features and functionalities.
- Integration with Existing Systems and Tools:
Integrate seamlessly with other enterprise systems and tools commonly used within the organisation, such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), and BI (Business Intelligence) platforms. Enable data exchange and interoperability to avoid silos and duplication of effort.
- Scalability and Performance Optimization:
Design for scalability to accommodate the growing needs of the organisation over time. Optimise performance by minimising load times, reducing latency, and efficiently managing resources, especially when dealing with large datasets and concurrent users.
- Feedback Loops and Continuous Improvement:
Establish feedback mechanisms to gather input from users and stakeholders throughout the design and development process. Iterate based on user feedback, analytics data, and usability testing to continuously improve the software’s UX and functionality.
What are the challenges of Enterprise software design?
Designing user interfaces (UI) and user experiences (UX) for enterprise software presents its own unique set of challenges compared to consumer-facing applications. Here are some of the key challenges:
- Complexity:
Enterprise software often deals with complex workflows and large amounts of data. Designers need to ensure that the UI doesn’t overwhelm users with too many options or information while still providing access to necessary functionalities.
- Diverse User Base:
Enterprise software typically serves a diverse user base with varying levels of technical expertise and job roles. Designing an interface that caters to the needs of different user personas can be challenging.
- Legacy Systems Integration:
Many enterprises have existing legacy systems that new software needs to integrate with. Ensuring a seamless experience between old and new systems while maintaining consistency in UI design can be a significant challenge.
- Security and Compliance:
Enterprises often deal with sensitive data and strict regulatory requirements. Designing UIs that prioritise security measures while still being user-friendly is crucial.
- Customization and Flexibility:
Enterprises often require software that can be customised to fit their specific needs and workflows. Designing UIs that are flexible enough to accommodate customization without sacrificing usability can be tricky.
- Scalability:
Enterprise software needs to be scalable to accommodate growing businesses and changing requirements. UI designs should be able to scale seamlessly without sacrificing performance or usability.
- Training and Onboarding:
Enterprise software typically requires training and onboarding processes due to its complexity. Designing intuitive UIs that reduce the learning curve and facilitate easy onboarding is essential.
- Cross-platform Compatibility:
Enterprises may have employees using different devices and platforms. Designing UIs that work seamlessly across various devices and screen sizes while maintaining consistency can be a challenge.
- Feedback and Iteration:
Enterprises often have hierarchies and multiple stakeholders involved in decision-making. Gathering feedback from all stakeholders and iterating on the design based on their input can be a time-consuming process.
- Return on Investment (ROI):
Enterprise software projects often require substantial investments. Designing UIs that improve productivity, efficiency, and user satisfaction, thus ensuring a positive ROI, is a key challenge for designers.
By applying these strategies, UX designers can create enterprise software solutions that empower users, streamline workflows, and drive business value within complex organisational contexts.
Placement of the week

Harsha lund - BMS
Aumnix Pvt ltd – UX UI Design Intern
It was a positive experience overall. I secured a placement soon after receiving the certificate, which was rewarding, I enjoyed the lectures; they were interactive and the instructor’s informal teaching style made the sessions enjoyable. They also provided valuable assistance with my portfolio and internship terms. I would recommend this program to newcomers in UI/UX who want to learn the basics of the field The instructor was available to clear doubts and provide guidance
Accessibility Audit Tools
Responsive Design Practices
User Onboarding Flows
Information Architecture
Cross Cultural Design Consideration
Sustainable Design Principles
Enterprise Software UX Design

The Statista report states that. 54.67% traffic comes from mobile devices in Q4 of 2024. User friendly design majorly influenced this, faster loading times and mobile friendly layouts.
Let us see one more stats..
The Design Management Institute studies shows the UX design companies helped in outperforming SP 500 companies by 228% over the last years.
This further establishes UX design understands users better and makes them feel we care for you. Thus, brand loyalty translates into dollar signs.
This can be further explained through this blog.But before that, you need to understand enterprise software design.
What is Enterprise Software UX design?
The Enterprise software UX design enhances user experience in system and software applications with eye on business needs.
Why does Enterprise UX matter?
Enterprise UX solves this problem differently by explaining it from the customer service person’s point of view. In the service centre, a customer raises a complaint. The customer service person then retrieves the customer details from the CRM and the plans details from another platform. This process can be tiring as they go back and forth.
How does Enterprise UX solve this problem differently?
The enterprise UX helps in streamline the process in a single tool thus resulting in
- Short business process with less room for errors.
- Efficient in customer and customer service person, thus resulting in providing better services.
- Less training for employees
As you got a gist about it. Let us further understand with more statistics
- According to WebFX, 94% of a brand website’s first impressions are related to design.
- According to Business Research Insights, the size of the worldwide UI market reached almost $1.6 billion in 2021 to $3.693 billion by 2028, exhibiting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 15.01%. Similarly, the global UX market, valued at $6,120.44 million in 2021, is forecasted to expand to $20,058 million by 2028, with a projected CAGR of 16.24%.
- Almost half (48%) say the number one way they decide on the credibility of a business is determined by the web design
- The Zippa report states that “38% of users won’t engage with a website if its layout is unattractive”
- According to a survey of top design firms, 50% of them consider website design for brand selection.
What are the strategies used in Enterprise software design?
UX design is used for complex enterprise software solutions that require a deep understanding of the intricate workflows, diverse user roles, and unique challenges inherent in such environments. Here are some specific strategies tailored to address these complexities:
- User Research and Persona Development:
Conduct rigorous user research to understand the needs, goals, and pain points of distinct user roles within the organisation. Create detailed user personas representing various stakeholders, including end-users, administrators, and decision-makers.
- Task Analysis and Workflow Mapping:
Analyse the complex workflows and business processes involved in the enterprise. Map out user journeys and identify key touchpoints where the software can streamline tasks, reduce friction, and improve productivity.
- Hierarchical Information Architecture:
Design a clear and intuitive information architecture that reflects the hierarchical structure of the enterprise. Organise features, modules, and data in a logical manner, for users to navigate easily and locate information relevant to their tasks.
- Customizable Dashboards and Views:
Provide users with customizable dashboards and views that allow them to personalise their workspace according to their preferences and priorities. Enable users to configure widgets, charts, and data tables to display the information most relevant to their roles.
- Contextual Awareness and Adaptive Interfaces:
Build interfaces that adapt dynamically based on the user’s context, preferences, and permissions. Surface relevant information and features based on the user’s current task, location within the software, and role within the organisation.
- Assistive Technologies and Accessibility:
Ensure that the software is accessible to users with disabilities by following standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). Provide support for assistive technologies such as screen readers, keyboard navigation, and voice commands.
- Progressive Disclosure and Guided Onboarding:
Employ progressive disclosure techniques to reveal complexity as users become more familiar with the software. Offer guided onboarding experiences and contextual tooltips to help users learn how to use advanced features and functionalities.
- Integration with Existing Systems and Tools:
Integrate seamlessly with other enterprise systems and tools commonly used within the organisation, such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), and BI (Business Intelligence) platforms. Enable data exchange and interoperability to avoid silos and duplication of effort.
- Scalability and Performance Optimization:
Design for scalability to accommodate the growing needs of the organisation over time. Optimise performance by minimising load times, reducing latency, and efficiently managing resources, especially when dealing with large datasets and concurrent users.
- Feedback Loops and Continuous Improvement:
Establish feedback mechanisms to gather input from users and stakeholders throughout the design and development process. Iterate based on user feedback, analytics data, and usability testing to continuously improve the software’s UX and functionality.
What are the challenges of Enterprise software design?
Designing user interfaces (UI) and user experiences (UX) for enterprise software presents its own unique set of challenges compared to consumer-facing applications. Here are some of the key challenges:
- Complexity:
Enterprise software often deals with complex workflows and large amounts of data. Designers need to ensure that the UI doesn’t overwhelm users with too many options or information while still providing access to necessary functionalities.
- Diverse User Base:
Enterprise software typically serves a diverse user base with varying levels of technical expertise and job roles. Designing an interface that caters to the needs of different user personas can be challenging.
- Legacy Systems Integration:
Many enterprises have existing legacy systems that new software needs to integrate with. Ensuring a seamless experience between old and new systems while maintaining consistency in UI design can be a significant challenge.
- Security and Compliance:
Enterprises often deal with sensitive data and strict regulatory requirements. Designing UIs that prioritise security measures while still being user-friendly is crucial.
- Customization and Flexibility:
Enterprises often require software that can be customised to fit their specific needs and workflows. Designing UIs that are flexible enough to accommodate customization without sacrificing usability can be tricky.
- Scalability:
Enterprise software needs to be scalable to accommodate growing businesses and changing requirements. UI designs should be able to scale seamlessly without sacrificing performance or usability.
- Training and Onboarding:
Enterprise software typically requires training and onboarding processes due to its complexity. Designing intuitive UIs that reduce the learning curve and facilitate easy onboarding is essential.
- Cross-platform Compatibility:
Enterprises may have employees using different devices and platforms. Designing UIs that work seamlessly across various devices and screen sizes while maintaining consistency can be a challenge.
- Feedback and Iteration:
Enterprises often have hierarchies and multiple stakeholders involved in decision-making. Gathering feedback from all stakeholders and iterating on the design based on their input can be a time-consuming process.
- Return on Investment (ROI):
Enterprise software projects often require substantial investments. Designing UIs that improve productivity, efficiency, and user satisfaction, thus ensuring a positive ROI, is a key challenge for designers.
By applying these strategies, UX designers can create enterprise software solutions that empower users, streamline workflows, and drive business value within complex organisational contexts.
Accessibility Audit Tools
Responsive Design Practices
Placement of the week

Harsha lund - BMS
Aumnix Pvt ltd – UX UI Design Intern
It was a positive experience overall. I secured a placement soon after receiving the certificate, which was rewarding, I enjoyed the lectures; they were interactive and the instructor’s informal teaching style made the sessions enjoyable. They also provided valuable assistance with my portfolio and internship terms. I would recommend this program to newcomers in UI/UX who want to learn the basics of the field The instructor was available to clear doubts and provide guidance
